B2 English Level (Upper-Intermediate)
- Key points of detailed texts
- Standard spoken language, whether live or broadcast
- Texts with extensive vocabulary and a high level of independence

B2 Upper Intermediate English Level
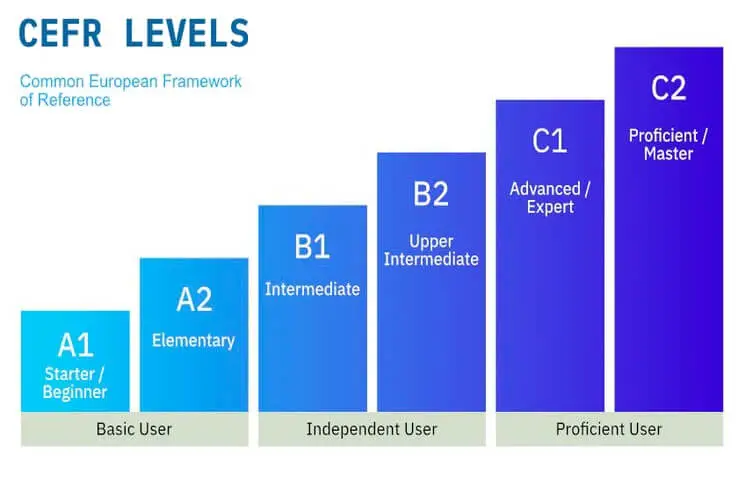
The Common European Framework of Reference (CEFR), a list of various language proficiency levels created by the Council of Europe, places English at level B2, which is the fourth level of English. This degree of proficiency could be described as “confident” in ordinary speech, as in “I am a confident English speaker.” The phrase “upper intermediate” is used to describe the level. Although with a restricted range of nuance and precision, students at this level can freely function in a variety of academic and professional situations in English.

What are the B2 Level Skills?
Level B2 is part of the Independent User Level, which is divided into two sublevels: First and Second Independent User Level (B1 and B2). Level B2 is intended to reflect the Advanced level specification. This level highlights the ability to argue effectively, i.e., the ability to explain and defend opinions in a debate, providing adequate explanations, arguments and comments, etc.
Can understand the main ideas in complex texts which deal with both concrete and abstract topics, even if they are of a technical nature, as long as they are within their field of expertise.
Can interact with native speakers with a sufficient degree of fluency and naturalness, so that communication is effortless for the interlocutors.
Can produce clear and detailed texts on a range of diverse topics, as well as defend your point of view on general topics, indicating the pros and cons or different options.
What will I be able to do after completing the B2 English Level?
Comprehension
Listening Comprehension
- Understand long speeches and lectures, and even follow complex arguments as long as the topic is relatively familiar
- Understand nearly all the news bulletins on the television and on current affairs programs
- Understand most films in which the language is spoken at a standard language level
Reading Comprehension
- Read articles and reports related to modern problems in which the authors express specific viewpoints
- Understand contemporary literary prose
Speaking
Oral Interaction
- Be able to participate in a conversation with fluency and spontaneity, which makes normal communication with native speakers possible
- Take an active role in debates based on daily situations, explaining and defending points of view
Oral Expression
- Present clear and detailed descriptions of a wide range of topics related to my speciality
- Explain my point of view on a topic, mentioning the advantages and disadvantages of different options
Writing
Written Expression
- Write clear and detailed texts on a wide range of topics related to their interests
- Write essays or reports conveying information or proposing reasons that support or refute a particular point of view
- Write letters that emphasize the importance given to certain facts and experiences
Achieving CEFR Level B2
At the B2 level there is a focus on effective argument. Students are able to account for and sustain their opinions in discussion by providing relevant explanations, arguments and comments. They can explain a viewpoint on a topical issue giving the advantages and disadvantages of various options and can develop an argument giving reasons in support of or against a particular point of view. They can take an active part in informal discussion in familiar contexts, commenting, putting their point of view clearly, evaluating alternative proposals and making and responding to hypotheses. They are able to hold their own effectively in social discourse and understand in detail what is said to them in the standard spoken language even in a noisy environment. They can initiate discourse, take their turn when appropriate and end a conversation when they need to, though they may not always do this elegantly. They can interact with a degree of fluency and spontaneity that makes regular interaction with native speakers quite possible without imposing strain on either party. There is a new degree of language awareness. They are able to correct mistakes if they have led to misunderstandings, can make a note of “favourite mistakes” and consciously monitor speech for it/them and generally they can correct slips and errors if they become conscious of them.
B2 Listening
Students can understand standard speech spoken at a normal rate and follow even complex lines of argument provided the topic is reasonably familiar. They can understand the essentials of lectures and most TV news and current affairs programmes and can understand the majority of films in standard dialect.
B2 Reading
At this level, students can understand articles and reports concerned with contemporary problems in which the writers adopt particular stances or viewpoints. They can understand contemporary literary prose and can adapt style and speed of reading to different texts and purposes, using appropriate reference-sources selectively.
B2 Speaking
Students can interact with a degree of fluency and spontaneity that makes regular interaction with native speakers quite possible. They are able to take an active part in discussion in familiar contexts and can account for and sustain views clearly by providing relevant explanations and arguments.
They can present clear, detailed descriptions on a wide range of subjects related to their field of interest, expanding and supporting ideas with subsidiary points and relevant examples. They can explain a viewpoint on a topical issue giving the advantages and disadvantages of various options.
B2 Writing
Students are able to write clear, detailed text on a wide range of subjects related to their interests. They can write an essay or report, passing on information or giving reasons in support of or against a particular point of view. They can write letters highlighting the personal significance of events and experiences.
B2 Grammar
Here are the key grammar topics covered at the B2 level:
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- Future Continuous Tense
- Future Perfect Tense
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense
- First, Second, and Third Conditional Sentences
- Mixed Conditionals
- Passive Voice (in various tenses)
- Reported Speech (complex)
- Relative Clauses (Defining and Non-defining)
- Gerunds and Infinitives (complex uses)
- Modal Verbs (deduction, speculation, obligation, advice, possibility)
- Inversion for Emphasis
- Cleft Sentences
- Comparative and Superlative Structures (advanced)
- Subjunctive Mood
- Emphatic Structures (using “do/does/did” for emphasis)
- Ellipsis and Substitution
- Linking Words and Phrases (cohesive devices for logical flow)
- Adverbial Clauses (time, reason, contrast, purpose)
- Participle Clauses
- Nominal Clauses
- Conditional Clauses (advanced uses and mixed conditionals)
- Phrasal Verbs (advanced and idiomatic uses)
B2 Vocabulary
B2 vocabulary includes a broader and more complex range of words and phrases that enable learners to discuss a wider variety of topics in more detail. Examples of B2 vocabulary include:
Work and Business:
Terms: productivity, efficiency, management, promotion, negotiation, contract
Phrases: “to meet a deadline,” “to hold a meeting,” “to negotiate terms,” “to be promoted”
Education and Learning:
Terms: curriculum, syllabus, academic, scholarship, internship, seminar
Phrases: “to enroll in a course,” “to attend a lecture,” “to submit an assignment,” “to apply for a scholarship”
Travel and Leisure:
Terms: itinerary, accommodation, reservation, tourist attraction, excursion, leisure activity
Phrases: “to make a reservation,” “to plan an itinerary,” “to go sightseeing,” “to book a flight”
Health and Fitness:
Terms: nutrition, wellness, diagnosis, treatment, therapy, rehabilitation
Phrases: “to follow a balanced diet,” “to receive a diagnosis,” “to undergo treatment,” “to engage in physical activity”
Technology and Innovation:
Terms: software, hardware, innovation, development, cybersecurity, digital
Phrases: “to upgrade software,” “to develop a new app,” “to ensure cybersecurity,” “to stay up-to-date with technology”
Environment and Nature:
Terms: conservation, pollution, ecosystem, biodiversity, climate change, renewable energy
Phrases: “to protect the environment,” “to reduce pollution,” “to preserve biodiversity,” “to use renewable energy”
Social Issues:
Terms: equality, discrimination, poverty, migration, human rights, community
Phrases: “to fight for equality,” “to address discrimination,” “to reduce poverty,” “to support human rights”
Adjectives:
Complex, descriptive adjectives such as: efficient, innovative, comprehensive, reliable, sustainable, flexible
Verbs:
Advanced verbs such as: analyze, assess, collaborate, innovate, negotiate, implement
Adverbs:
Frequency and degree adverbs such as: frequently, occasionally, significantly, considerably, relatively, increasingly
Phrasal Verbs:
More complex phrasal verbs such as: come up with, get along with, look forward to, put up with, run out of, take over
Idiomatic Expressions:
Examples: “break the ice,” “hit the nail on the head,” “burn the midnight oil,” “jump on the bandwagon,” “bark up the wrong tree”
Collocations:
Common collocations such as: “make a decision,” “take responsibility,” “have an impact,” “raise awareness,” “pay attention”
What is possible with an B2 English level?
You could work in an English-speaking environment if you had a B2 level of proficiency, and many non-native English speakers in global workplaces do. However, a B2 level English speaker will be lacking in nuance, especially outside of his own profession. Additionally, he might overlook some of the intricacies and implied meanings in speech.
The official CEFR rules state that someone with an English language proficiency of B2:
- possesses the ability to comprehend the major concepts of complicated texts on both concrete and abstract issues, including technical talks in their area of expertise.
- can communicate with native speakers with a level of spontaneity and fluency that allows frequent interaction with them possible without any stress on either party.
- can write content that is both clear and informative on a variety of topics and convey a point of view on a current issue by weighing the benefits and drawbacks of several options.
Detailed B2 English proficiency
For educational purposes, the official can-do statements are divided into more manageable chunks. You can evaluate your own English proficiency using this more thorough skill breakdown, or a teacher can use it to evaluate a student’s proficiency.
A student with a level B2 in English, for instance, will be able to do everything a level B1 student can do as well as the following in addition:
- Participate in sessions related to your area of expertise if you need assistance with certain concepts.
- Discuss how cultural norms and perceptions of rudeness connect to gender issues.
- Talk about your personal finances and provide friends and coworkers financial advice.
- Describe your personal and professional lives, including your daily activities at work.
- Describe your background, experience, strengths, and limitations while also going over your career goals.
- Discuss your thought processes and how you might use them to be more effective at work.
- Talk about the books you enjoy reading and offer suggestions for good books.
- in social circumstances, use acceptable words, including complimenting and showing sympathy.
- Talk about your favorite leaders and leadership traits.
- deal with difficult circumstances that can be rather complex that come up in social and professional settings.
- Describe typical political circumstances and political behavior.